What is SPRAVATO (Esketamine) Nasal Spray for Depression Treatment?
Esketamine nasal spray is derived from the anesthetic ketamine, which has a long history of being used to treat Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and treatment-resistant depression. It’s the first and only FDA-approved treatment for depression that targets the glutamate system.
SPRAVATO treatment comes in the form of a nasal spray. Because SPRAVATO (Esketamine) is considered a controlled substance, it must be administered by specially trained medical personnel in a certified clinical setting who can monitor for side effects of SPRAVATO while ensuring patients see the most beneficial results. Most patients receive their esketamine treatment as an outpatient and go home in a couple of hours.
Antidepressants Aren’t Always the Answer
1 in 3
people struggling with depression have Treatment-Resistant Depression (TRD), meaning they don’t respond to medications.

Recovery
with SPRAVATO (Esketamine) nasal spray treatment is 2.5x more likely for patients who failed 2+ medications.
Is esketamine nasal spray an option for you?
Have you had an unsatisfactory response to antidepressants or is an antidepressant not working at all? Are you experiencing unpleasant side effects, or have learned that you cannot tolerate them? If so, esketamine treatment is an alternative form of mental health care that can help you find relief from depression symptoms.
Currently, FDA approval allows for SPRAVATO (Esketamine) to be used together with oral antidepressants, and only for patients who meet specific criteria, which include:
- Patients have tried at least two other antidepressants for a minimum of six weeks each, and have not experienced remission, or
- Patients did not have at least a 50% improvement in mood or depressive symptoms.
Once one or both of these conditions are met, providers can discuss incorporating SPRAVATO treatment into the patient’s customized treatment plan if:
- Their provider believes that SPRAVATO (Esketamine) therapy could work for them and their unique needs for depression or other mental health care.
- The patient is comfortable with trying SPRAVATO nasal spray.
If all the pieces fit, SPRAVATO therapy can be an excellent treatment option for depression.
How does SPRAVATO (Esketamine) nasal spray treatment work?
Like antidepressants, SPRAVATO (Esketamine) depression treatment raises the levels of certain chemicals like dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin that occur naturally in the brain as neurotransmitters. However, unlike oral antidepressants, SPRAVATO treatment increases the brain’s most prevalent chemical messenger: glutamate levels, thereby creating new connections in the brain in order to rapidly improve symptoms. This results in a greater reach and more substantial impact on brain cells with a single dose compared to antidepressants.
SPRAVATO Treatment Patient Results at Mindful Health Solutions
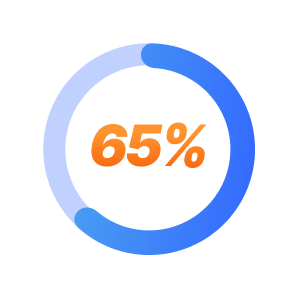
65% of TRD patients respond positively to SPRAVATO within 6 weeks.
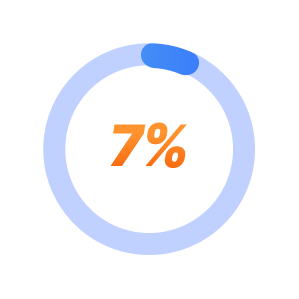
7% chance of success with trying a 4th medication.*
*STAR-D trial
What Our Patients Are Saying about Esketamine Nasal Spray
“It gives you a little bit of space between yourself and your problems or your trauma.”
Why Mindful Health Solutions for Esketamine Treatment?
SPRAVATO (Esketamine) nasal spray is a fairly new treatment for depression, and not everyone can provide the same expert and safe medical care as we can at Mindful Health Solutions. As one of the nation’s top SPRAVATO treatment providers for depression care, we have the knowledge and expertise to help you achieve relief and happiness. Our experienced clinical leadership team has been applying innovative treatment protocols through SPRAVATO (Esketamine) nasal spray for years supported by positive outcome data. In fact, Mindful Health Solutions has one of the largest SPRAVATO (Esketamine) patient outcome repositories in the world, with more than 35,000 treatment visits to track our patients’ progress in real time and develop algorithms that help predict the probability of successful interventional treatment outcomes.
Our expert clinical team is committed to helping you find happiness, and will only recommend Spravato (Esketamine) as a treatment option if we believe it will help you finally experience relief. All treatments are administered in a comfortable outpatient setting, ensuring safety and minimal side effects of SPRAVATO. Trust Mindful Health Solutions for safe, effective SPRAVATO therapy on your path to mental wellness – it is our mission to provide innovative and effective care, helping you overcome the challenging symptoms of depression and find joy again.
Frequently Asked Questions
How effective is SPRAVATO therapy?
Unlike most antidepressants that can take several weeks to show effects, SPRAVATO (Esketamine) nasal spray often begins to alleviate symptoms within a few weeks and sometimes even days. Many patients report a rapid improvement in mood and outlook after treatment.
How is SPRAVATO (Esketamine) administered?
Each esketamine treatment is administered in our certified SPRAVATO clinics. At the clinic, patients self-administer the nasal spray in a relaxed setting. They are then monitored for side effects of SPRAVATO as well as to ensure optimal results, for at least two hours prior to leaving the clinic.
How do you feel during esketamine therapy?
During treatment, you may feel dissociation, which is a common effect of SPRAVATO (Esketamine). The experience of dissociation can vary from person to person but may include:
- Feeling detached from your body
- Having a distorted perception of time and space
- Experiencing altered perceptions and sensations
- Entering a dream-like state where thoughts may become distorted
- Emotional detachment
Some individuals describe a sense of mental clarity or expanded consciousness.
Is SPRAVATO (Esketamine) covered by insurance?
Yes, SPRAVATO (Esketamine) for depression is covered by insurance with prior authorization by your insurance company. Mindful Health Solutions is in-network with Kaiser, Medicare, and most major commercial insurance plans. Contact us to discuss SPRAVATO cost and insurance coverage options.
Eligibility:
- Adults 18+
- Major Depressive Disorder diagnosis
- 2+ antidepressant failures OR intolerable side effects to medication
When will I start to notice results from SPRAVATO (Esketamine) treatment?
Many patients observe a significant improvement after 3 to 8 treatments, with some achieving remission by the 12th esketamine nasal spray treatment. It’s important to keep in mind that each person’s experience with this depression care therapy is unique.
Are there any side effects of SPRAVATO?
The most common side effects of SPRAVATO usually only occur within one to two hours after the nasal spray has been administered. To help ensure the safety of patients, there is a two-hour window of supervision at the clinic following the administration before patients can leave and head home. These side effects include:
- Sleepiness
- Nausea
- Increased blood pressure
- Bad taste in mouth
- Disassociation
What is the treatment schedule for SPRAVATO (Esketamine)?
For Spravato (Esketamine) to become included in your customized treatment plan, our staff will gather information on your symptoms and background, as well as any treatments you have attempted. They will answer any questions you may have and, if you are interested, discuss how the treatment works. From there, you will be able to schedule your treatment sessions.
The FDA-approved treatment plan for SPRAVATO (Esketamine) involves attending sessions twice a week for the first 4 weeks, followed by weekly sessions for the next 4 weeks. We also recommend a tapering protocol and maintenance treatments to help sustain remission. The complete FDA-approved protocol includes 12 treatments, assuming you tolerate the medication well. Your physician will also help you to determine maintenance treatments based on your unique needs.
All treatment plans at Mindful Health Solutions are customized to each patient. Our talented team of clinicians and support staff is dedicated to working with patients collaboratively to find a treatment plan that works for them. Our goal is to help patients find relief in a way that feels good.
Is SPRAVATO (Esketamine) used to treat anything other than depression?
While esketamine therapy is only FDA-approved for adult treatment-resistant depression and MDD with acute suicidal ideation, it can also help with other mental health conditions. Many people who get SPRAVATO (Esketamine) for their depression also experience other conditions like OCD, anxiety, or an eating disorder.
Our Chief Medical Officer, Dr. Tobias Marton, explains, “In my experience, it is sort of a ‘rising tide lifts all boats’ kind of thing. As your depression gets better, other aspects of your mental health get a little bit better as well.”
Again, SPRAVATO (Esketamine) is only approved for depression. However, it is possible that you may experience relief in other areas of your mental health when going through treatments.
The FDA-approved treatment plan for SPRAVATO (Esketamine) involves attending sessions twice a week for the first 4 weeks, followed by weekly sessions for the next 4 weeks. We also recommend a tapering protocol and maintenance treatments to help sustain remission. The complete FDA-approved protocol includes 12 treatments, assuming you tolerate the medication well. Your physician will also help you to determine maintenance treatments based on your unique needs.
All treatment plans at Mindful Health Solutions are customized to each patient. Our talented team of clinicians and support staff is dedicated to working with patients collaboratively to find a treatment plan that works for them. Our goal is to help patients find relief in a way that feels good.
For Providers: Can I refer a patient for SPRAVATO (Esketamine)?
Yes! We offer a simple referral process. After you refer your patient to Mindful Health Solutions for esketamine therapy, we'll take care of the rest.
- Assign treatment specialist to provide full support
- Handle insurance authorization
- File claims for treatments on behalf of your patient
- Consultation with providing clinician on the treatment process
- Schedule your patients based on their lifestyle needs
- Clinician closely monitors patients throughout treatment
- Collaboration with referring provider and stakeholders
- Patient returned to referring provider for continuation of care
Our Chief Medical Officer, Dr. Tobias Marton, explains, “In my experience, it is sort of a ‘rising tide lifts all boats’ kind of thing. As your depression gets better, other aspects of your mental health get a little bit better as well.”
Again, SPRAVATO (Esketamine) is only approved for depression. However, it is possible that you may experience relief in other areas of your mental health when going through treatments.
The FDA-approved treatment plan for SPRAVATO (Esketamine) involves attending sessions twice a week for the first 4 weeks, followed by weekly sessions for the next 4 weeks. We also recommend a tapering protocol and maintenance treatments to help sustain remission. The complete FDA-approved protocol includes 12 treatments, assuming you tolerate the medication well. Your physician will also help you to determine maintenance treatments based on your unique needs.
All treatment plans at Mindful Health Solutions are customized to each patient. Our talented team of clinicians and support staff is dedicated to working with patients collaboratively to find a treatment plan that works for them. Our goal is to help patients find relief in a way that feels good.
