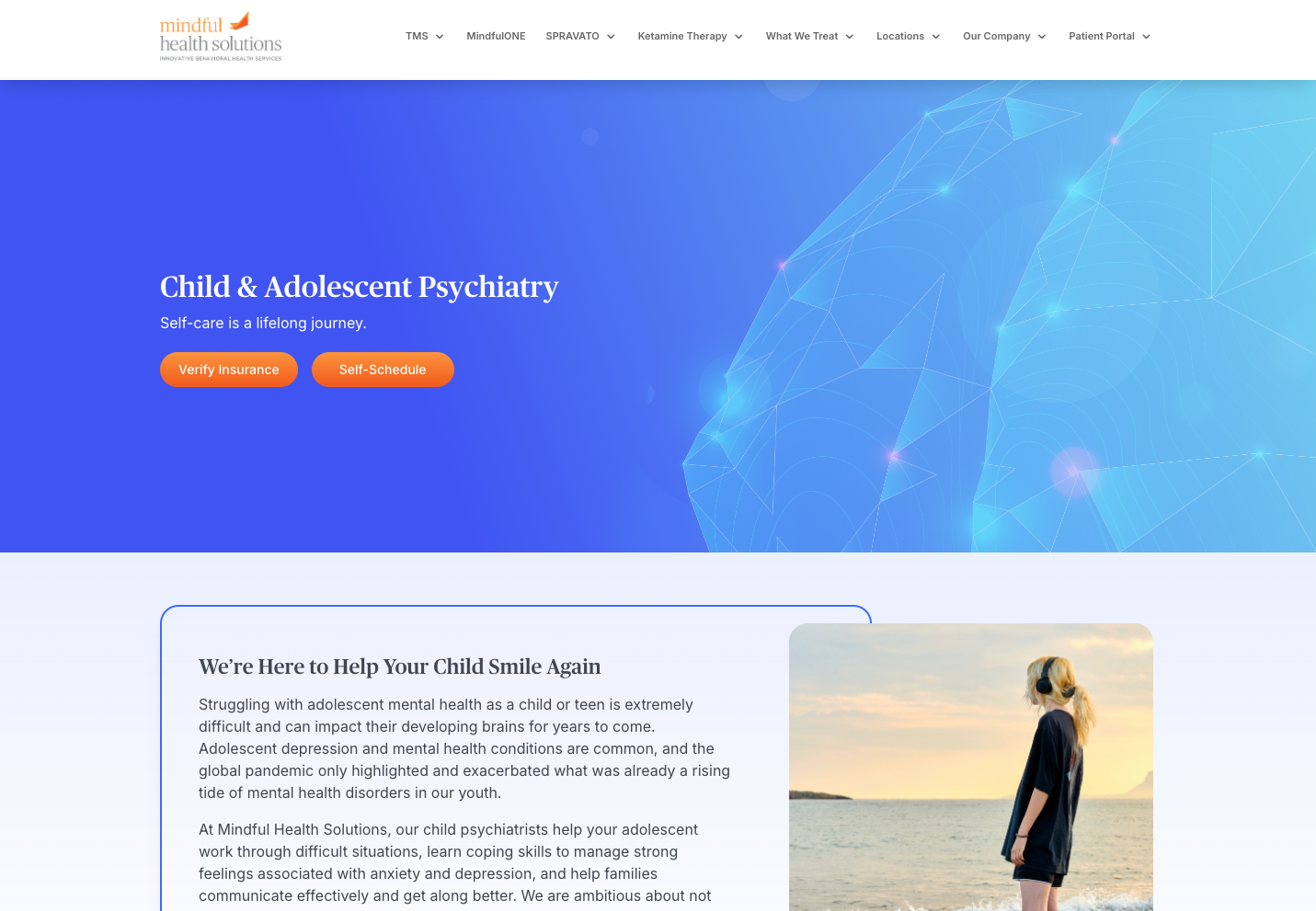
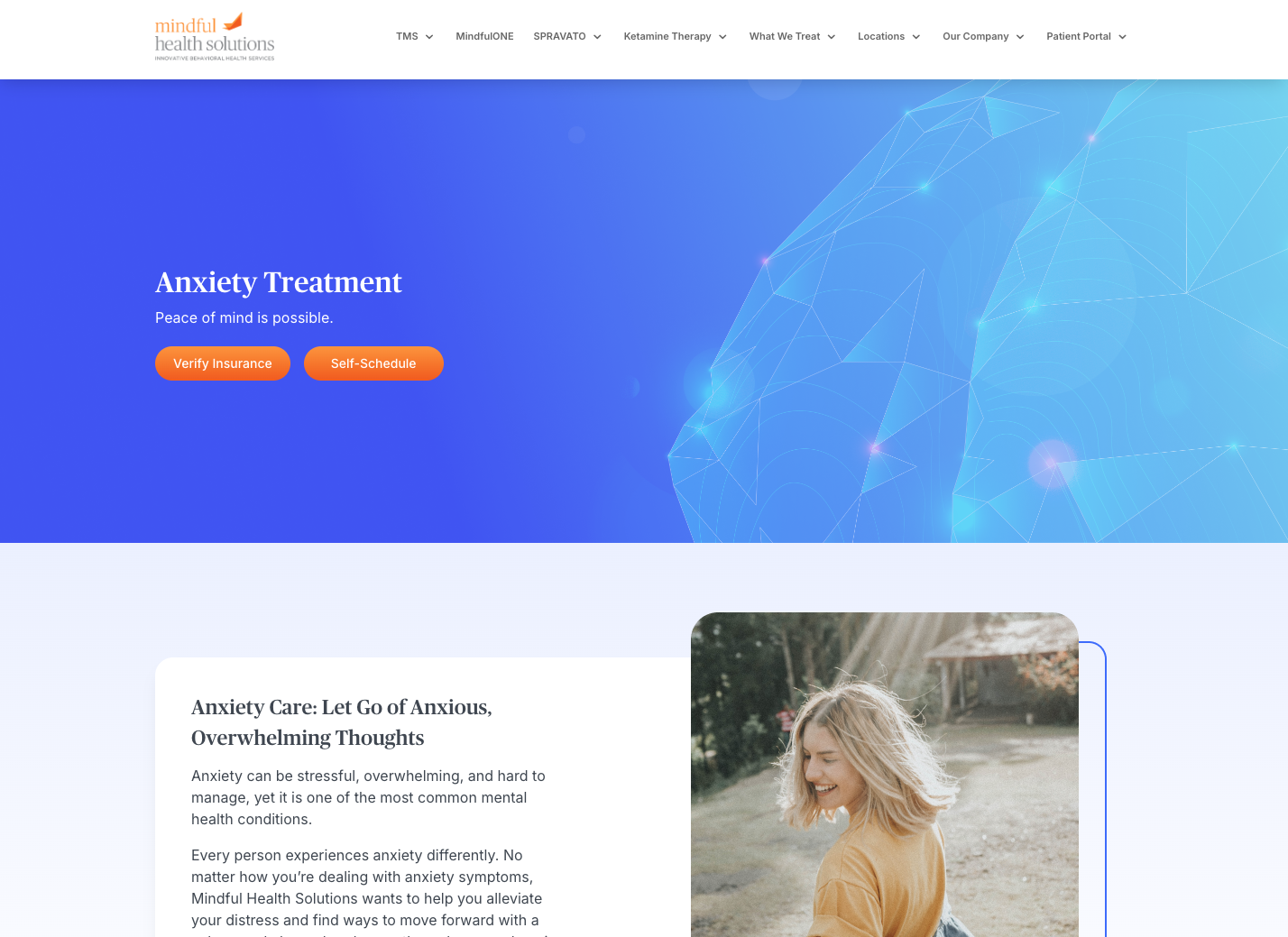
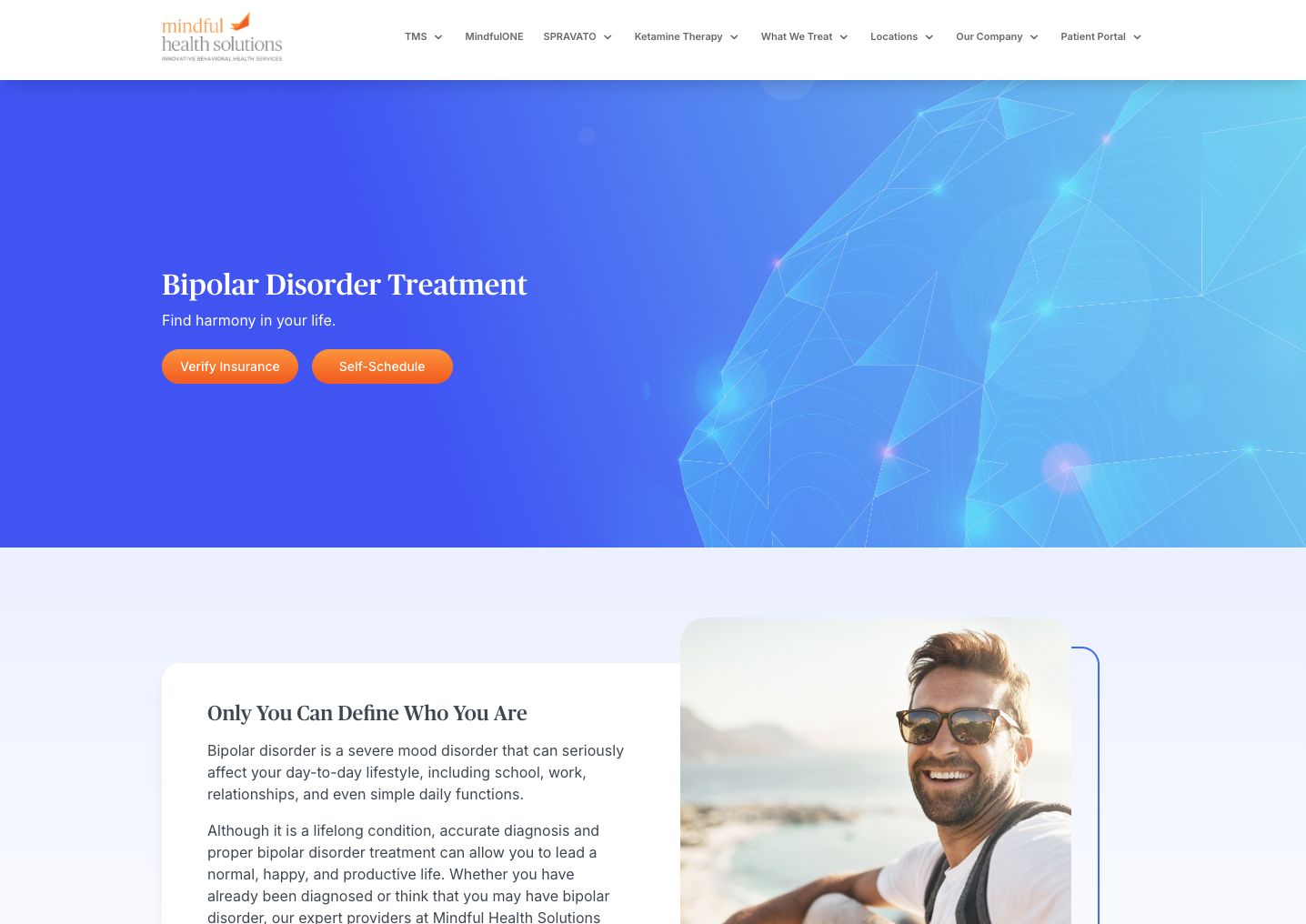
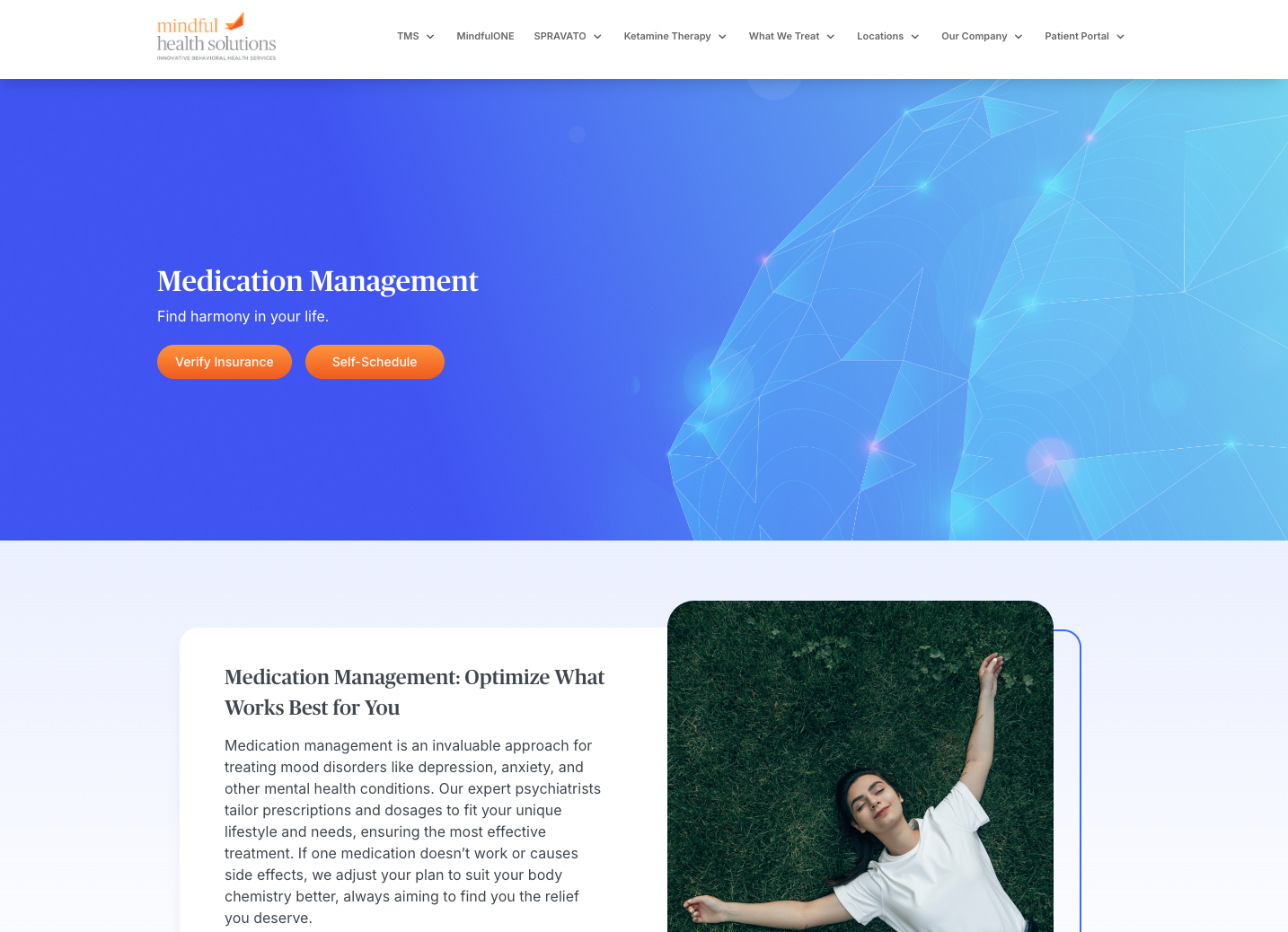
Benjamin Williamson, MD
Dr. Benjamin Williamson is a board-certified psychiatrist in Newport Beach whose areas of focus include the medical treatment of severe depression and anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, social anxiety disorder, and bipolar disorder.

More about Benjamin Williamson
In his work with patients, Dr. Williamson takes a special interest in the mind-body connection and emphasizes the importance of physical health for mental well-being. He is vigilant in investigating potential co-morbid medical problems that could exacerbate psychiatric symptoms. For example, depression, poor concentration, anxiousness, poor sleep, fatigue, and low energy are non-specific symptoms that may be associated with a major depressive disorder and obstructive sleep apnea. He believes that it is of paramount importance to screen for co-morbid physical disease states that can worsen psychiatric symptoms.
Dr. Williamson sees his role as that of expert consultant. He wants his patients to be fully informed about their options for treatment and, especially, what risks are associated with available treatments. Each patient has unique values and goals for treatment, and he wants to put them in a position to make the best decision for them.
Having treated patients with severe and complicated forms of depression, he has seen the limitations of pharmacotherapies. Sometimes patients do not respond well, even to multiple medications at high doses. Medications, even when they do work, can cause troublesome side effects. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy in Newport Beach patients has proven to be effective for many people and is not associated with the side effects that sometimes limit the use of medications. Moreover, there is promising clinical research for the use of TMS in treating psychiatric conditions other than depression.
Personal Interests
Living in Southern California gives Dr. Williamson the opportunity to escape to the natural world of its beaches and wilderness areas while staying close first-class artistic and cultural institutions. He loves the California sun, gorgeous weather, and beautiful landscapes. He also enjoys having close access to top-notch stage productions at our many community theaters. As an avid reader, he reads a lot of psychiatric journals to keep up with the rapidly growing body of knowledge in psychiatry.
Education & Experience
Certifications & Memberships
- As Seen on Psychology Today
- The Medical Board of California, License Number A162939
- American Psychiatric Association, License Number 70738
- Carlsbad, CA, Master of Psychopharmacology Program from the Neuroscience Education Institute (NEI)
- Board Certified in Adult Psychiatry, American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology
- Member, Clinical TMS Society
Publications
The Pharmacological Treatment of Tobacco Use Disorder. Grand Rounds Presentation. Wayne State University School of Medicine. Sept 2014.
Implementation of an Evidence-Based Treatment of Tobacco Use Disorder with Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) in an Inpatient Psychiatric Unit. Poster Presentation. Detroit Medical Center Department of Quality and Safety 4th Annual Quality Education and Safe Systems Training Research Day Poster Competition. Detroit, MI. Feb 2015
Implementation of an Ambulatory Alcohol Detoxification Protocol. Poster Presentation. American Psychiatric Association 168th Annual Meeting. Toronto, ON. May 2015.